Deorbit concepts have been proposed for dealing with the growing problems posed by orbital debris. Most devices use large structures that interact with the atmosphere, magnetic field, or solar environment to deorbit large objects more rapidly than natural decay. Some devices may be better than others relative to the likelihood of collisions during their use. Current guidelines attempt […]
Category: Professional Papers
A collection of Professional Papers from Global Aerospace Corporation
Aerodynamic and Mission Performance of a Winged Balloon Guidance System
A winged balloon guidance system exploits the natural wind-field variation with the altitude available in planetary atmospheres to generate passive lateral control forces on a balloon using a tether-deployed aerodynamic surface below the balloon. Several balloon guidance system topics are discussed,including development status,physics and aerodynamics,systems performance, concept of operations,and the near-space applications of this technology for scientific,communications,and defense applications. […]
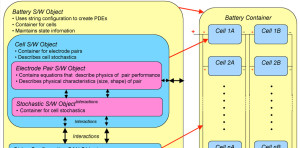
Dakota, a First Principles-based Battery Simulation and Modeling System
ABSTRACT Global Aerospace Corporation (GAC), in collaboration with its research partners, has been developing a state-of-the-art, object-oriented, first-principles-based simulation system, called Dakota, that can reproduce the actual behavior and performance of Li-Ion cells and batteries under a variety of operating conditions. As a desktop modeling and simulation system, Dakota is designed to describe and predict performance under various operational modes and environments. The […]
Gossamer Orbit Lowering Device (GOLD) for Safe and Efficient CubeSat Deorbit
Presentation: CubeSat Workshop, Logan, UT, August 8-9, 2015 Download Presentation
STRATOSPHERIC SATELLITES FOR EARTH OBSERVATIONS
Very long-duration stratospheric balloon platforms could provide revolutionary Earth observations for a fraction of the cost of competing platforms, such as stratospheric unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and airships and space satellites. Full Paper
Human Mars Exploration Transportation: Bridging Concept of Operations
A bridging architecture between a sustained Lunar exploration architecture and a sustained Mars transportation architecture is presented. The Mars architecture assumes sustained Mars operations as a final goal. A bridging Mars exploration transportation Concept of Operations (CONOPS) was developed. We describe the needed Earth/Moon system architecture, the sustained Mars system infrastructure, and the bridging Mars transportation infrastructure. Three trade space […]
An Express Transportation Architecture for Human Mars Exploration
If future plans for human space travel include recurring visits to a Mars Base for research and exploration, an efficient and fast transportation system will be crucial for rotating crews back and forth between Earth and Mars and to resupply needed equipment and fuels. An innovative interplanetary transportation architecture is described that uses highly autonomous, solar-powered, ion-propelled Astronaut Hotels, […]
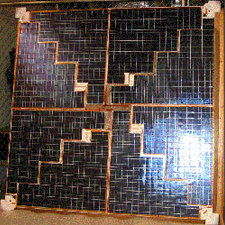
HIGHPOWER™ SOLAR ARRAY SYSTEM FOR BALLOONS
ABSTRACT A lightweight solar array pointing system is under development for application to balloons. The system suspends solar panels from their corners by cables. By raising and lowering diagonally opposite corners, the parallel solar panels can be simultaneously pointed to any point more than 20 degrees above horizontal. The system acts as a two-dimensional Venetian blind. The system eliminates the need for slip rings, […]
Mars 2001 Aerobot/Balloon System Overview
Abstract In late 1995, a study was initiated at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) of a 2001 Mars Aerobot/Balloon System (MABS) Mission Participants included NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Wallops Flight Facility (WFF), Lockheed Martin Aeronautics (LMA), the French Space Agency (CNES) Toulouse Space Center, NASA Ames Research Center (ARC), and Space Dynamics Laboratory (SDL) plus numerous industrial partners. The purposes of the study […]
VENUS GEOSCIENCE AEROBOT STUDY
The Venus Geoscience Aerobot Mission Study (VEGAS) was a four-month analysis of a semiautonomous, altitude-controlled balloon mission to Venus. The study focuses on a Delta launch in the 2007 timeframe, with a nominal 100-day balloon mission and orbiter telecom relay. After the initial balloon and payload deployment in the Venusian atmosphere, the balloon is capable of repeated excursions from altitudes of 60 […]
Gossamer Orbit Lowering Device for Safe and Efficient De-orbit
An inflatable de-orbit system that accelerates natural orbit decay by orders of magnitude is discussed